5 Russian lakes to search for monsters

Lake Labynkyr. Source: karpukhins.livejournal.com
Nessie’s brother from Lake Labynkyr
Lake Labynkyr is located at an altitude of 1,020 meters (3,346 feet) above sea level, and its depth is 52.6 meters. The lakebed has an anomalous fissure, with a depth that reaches 75–80 meters.
Locals only ever refer to the lake as “The Second Loch Ness.” Viktor Tverdokhlebov, local lead researcher of a team from the East-Siberian Section of the Soviet Academy of Science, recorded in his notes a sighting of an unidentified animal floating on the lake’s surface and resembling a giant fish.
“It was moving in an arc, at first along the lake, and then it came toward us... a dark-grey, oval-shaped body moved across the water. Against this background could be made out two symmetrical white spots, which could be eyes, and standing up on its body was something like a stick — perhaps a fin.
We only saw a small part of this animal, but we could imagine there was a massive body in the water. It was undoubtedly a predator — one of the most powerful predators in the world,” wrote Tverdokhlebov.
Very possibly, this report by a respected scientist has made the Lake Labynkyr Monster one of the more serious contenders for the role of a Second Nessie, even though the Russian Geographical Society (RGS) has rejected media reports of an alleged large animal jawbone located on the bed of the lake.
Raspberry Lakes
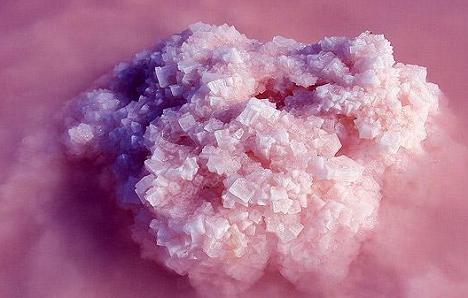
Not far from Astrakhan are the so-called “Raspberry Lakes.” They are noticeable not only for their color, but also for their distinct raspberry-like scent.
This was one reason why salt extracted from the lakes in hundreds of tons each year was considered the best in the land and delivered to the table of Russian Empress Catherine the Great.
Raspberry Lake. Source: x-trail.club.ru
This salt retains a pale pink color, along with the faint tang of raspberries. The color and aroma of salt in these waters are due to tiny crustaceans called “ Artemia .” When they die and decompose, they give a unique fragrance to the salt water. These crustaceans are a favorite item in the diet of flamingos.
The Brosno Dragon
The Russian Ogopogo — a mythical animal known only from reported sightings — lives in Lake Brosno, located in Tver Region. There have been no scientifically confirmed sightings of the beast, but legend would have us believe this is another Nessie.
As the story goes, the Brosno Dragon is a large, lizard-like plesiosaur — an object of fascination for many crypto-zoologists all over the world.

Lake Brosno. Source: club.photo.ru
Credence for the legend of these lake lizards is strengthened by the lake’s unusual depth: at 41 meters (134.5 feet) it is the deepest lake in the Tver Region. The decaying detritus on the lakebed, which causes bubbles of hydrogen sulphide to rise to the surface, also adds eerie believability to the story. From a distance, the bubbles give the impression of something moving in the middle of the lake.
Prehistoric animals in Elgygytyn Lake
Elgygytyn Lake is found 500 kilometers (310 miles) to the northwest of Anadyr, which is the capital city of Chukhotka — the farthest-flung region of Siberia. The lake area measures 120 square kilometers (46 square miles), and its depth in some places reaches 170 meters (557 feet).
Analysis of sediment at the bottom puts the lake’s age at 3.5 million years old. Despite its extreme northern location, the lake has never been covered in glaciers — suggesting the presence of some unknown, primordial, life traces in its waters.

Lake Elgygytgyn. Source: positime.ru
Of course, local people have come up with a number of legends of the existence of a “great beast” living in Elgygytyn Lake.
The formation of Elgygytyn Lake is something of a mystery itself. It is perfectly circular in shape, and American scientific journals have speculated that it was formed by a falling meteorite. Alternative theories have posited that the lake basin might be the crater of an extinct volcano.
Homes, churches, bell towers and more, on the bed of Lake Svetloyar
Lake Svetloyar is a small lake in the forests of Nizhny Novgorod Region, just 12 square kilometers in size (4.6 square miles). In terms of its makeup, it closely resembles other lakes formed 12,000–14,000 years ago at the end of the Ice Age.
Lake Svetloyar is one of Russia’s most mysterious lakes. Nothing is normal about it — from the unusual water, the pure taste of which remains unchanged over long years, to the peculiar legend of the city of Kitezh, which mysteriously sank underwater when the Tatar–Mongol army of Batu Khan came to besiege its walls.

Lake Svetloyar. Source: Lori Images / Legion Media
Geologists cannot agree on Lake Svetloyar’s origins, despite research that has dragged on for half a century. Some claim it formed on karst systems, which would be a blow to the idea of a city of Kitezh that voluntarily submerged beneath the waters.
Still others claim the lake is formed of solid rock, which is typical for the western part of Russia. Yet this rock structure is lined with faults, and Lake Svetloyar lies at the intersection of two such faults. This would mean that islands, which hypothetically stood in the lake, could indeed be submerged below the water in one of the faults. One such island might have been the site of the legendary city of Kitezh.
All rights reserved by Rossiyskaya Gazeta.
Subscribe
to our newsletter!
Get the week's best stories straight to your inbox
.png)