How were manicures done in the USSR?
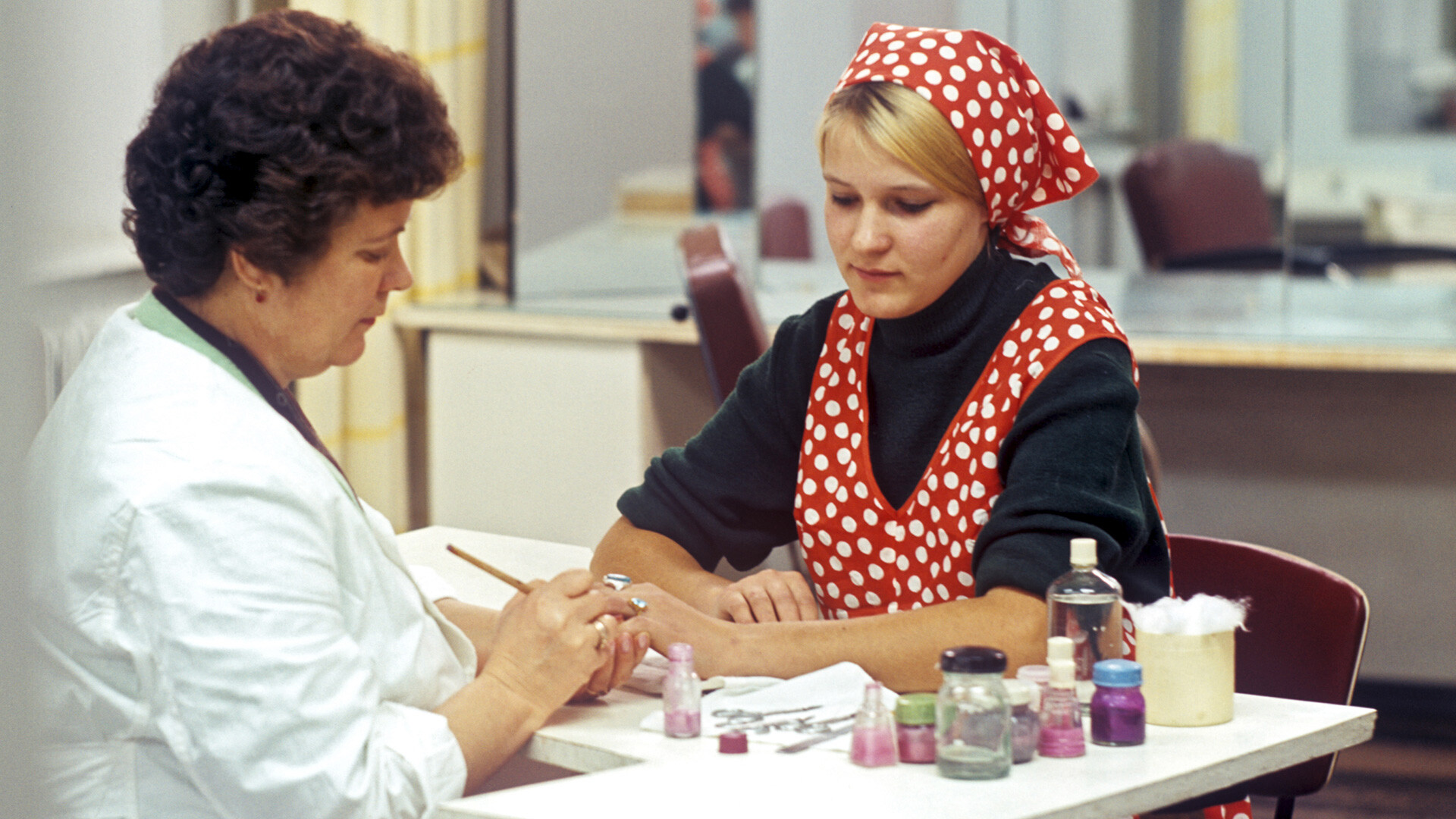

Today, many women in Russia already can’t imagine their life without a trip to a manicure salon, because, according to them, the nails are also “the face”. However, this phenomenon is not so new even in Russia. Nail technicians worked here fifty and even a hundred years ago.
Where was a manicure done?
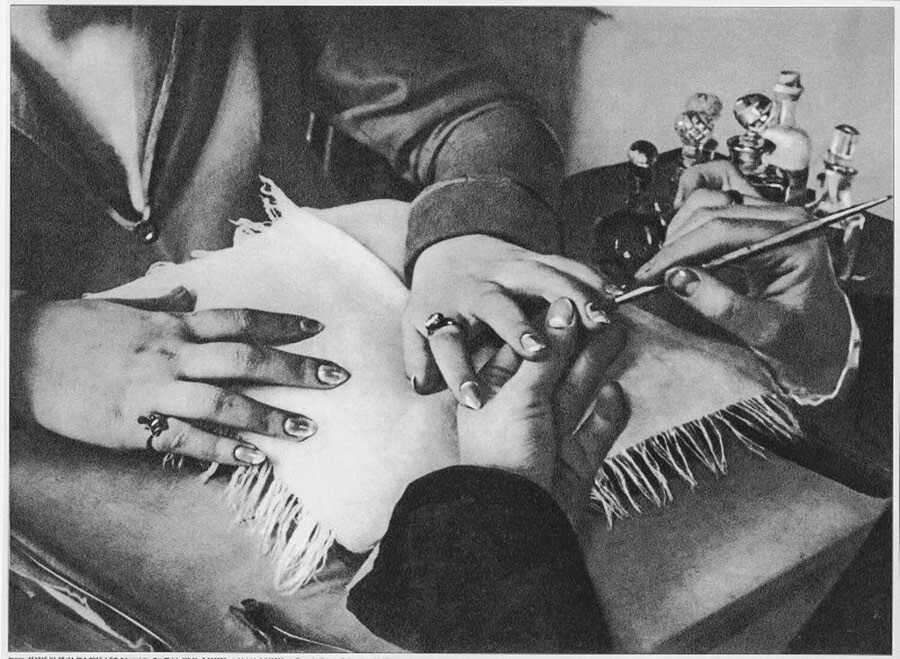 At the nailmaker's, 1926.
At the nailmaker's, 1926.
In the Soviet Union, there were no beauty salons in our modern understanding, but there were hair salons with manicure tables. And there were no lesser lines to good specialists than today, because Russian women have, at all times, striven to be beautiful. Most certainly, there weren’t many modern tools available back then (like the now famous ‘Russian manicure’ that uses an electric filer to open up the eponychium to remove the cuticle).
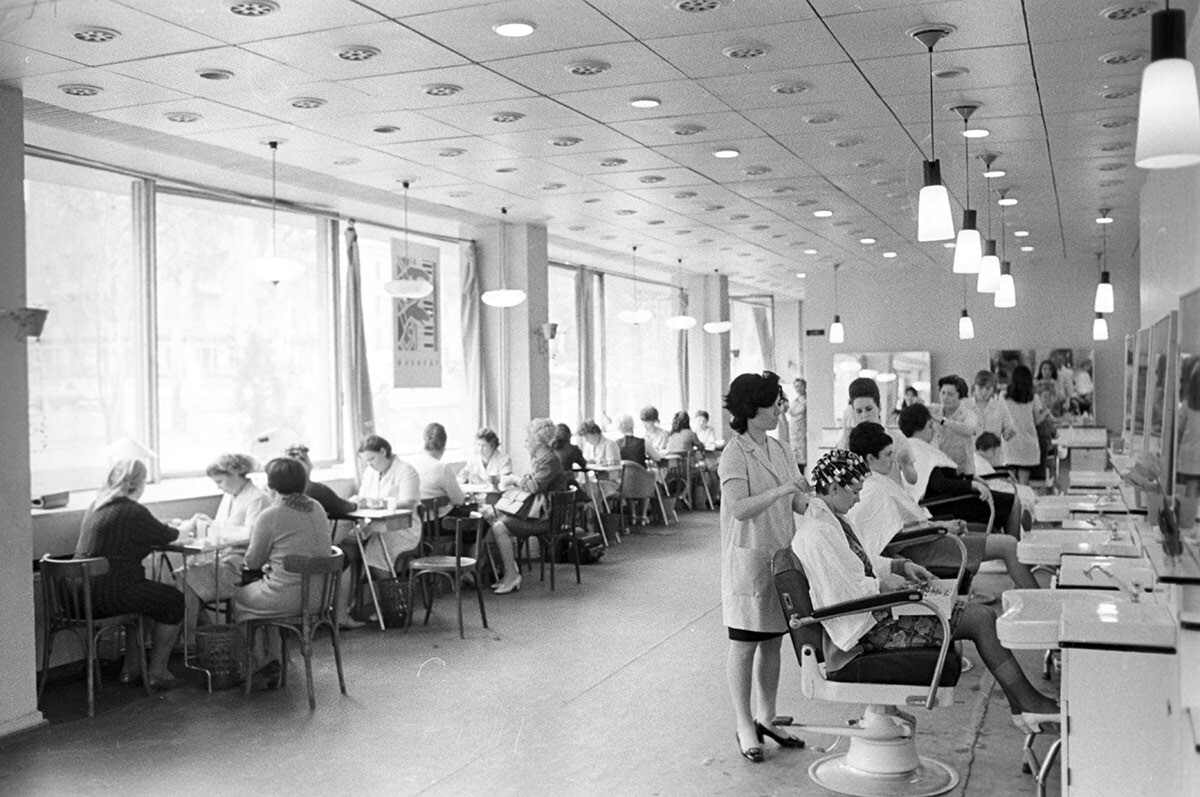 Beauty salon of Alma-Ata. 1971.
Beauty salon of Alma-Ata. 1971.
A professional manicure included several stages. The nails were first shaped, then the hands were soaked in soapy water to make the cuticles softer. Then, the nails were trimmed with tweezers and scissors. If a woman wanted, her nails could also be coated. However, there were no gel polishes at the time; but there were some ordinary Soviet-produced polishes. Their production was established in the 1930s.
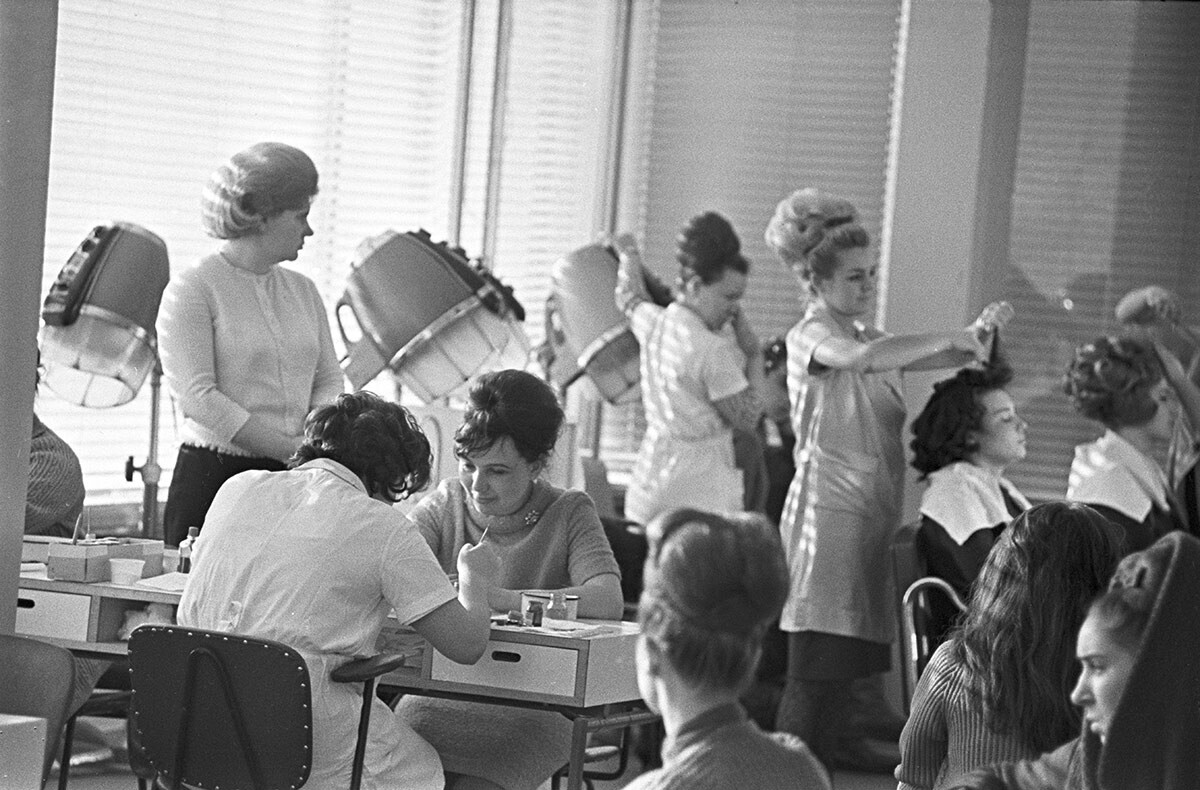 Soviet barbershop. 1967.
Soviet barbershop. 1967.
What kinds of nail polishes were there?
In the wartime 1940s, there were clearly things other than polishes to worry about, but in the decades that followed, the Soviet industry successfully produced a variety of colors and shades. Even today, you can find advertisements on the Internet for Soviet nail polishes from 50 years ago for sale and many are well preserved. The most common ones are polishes that were produced in Moscow and Leningrad (now St. Petersburg).
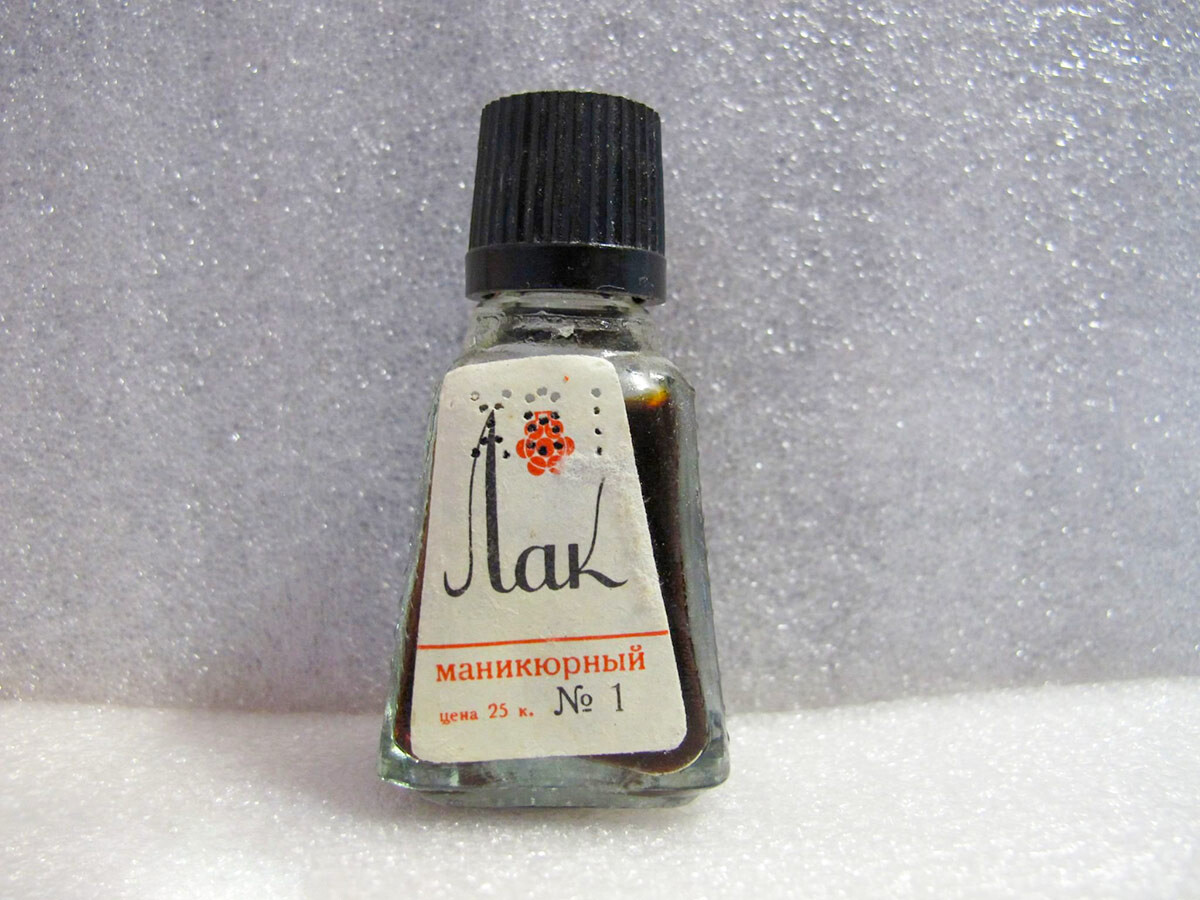 Soviet nail polish.
Soviet nail polish.
Polishes from the middle of the last century were most often either reddish or of nude shades. To paint nails in dark (or even black) colors was considered indecent and even vulgar. Pink and beige were for everyday wear, while red was well suited for special occasions. Transparent varnishes were also in use.
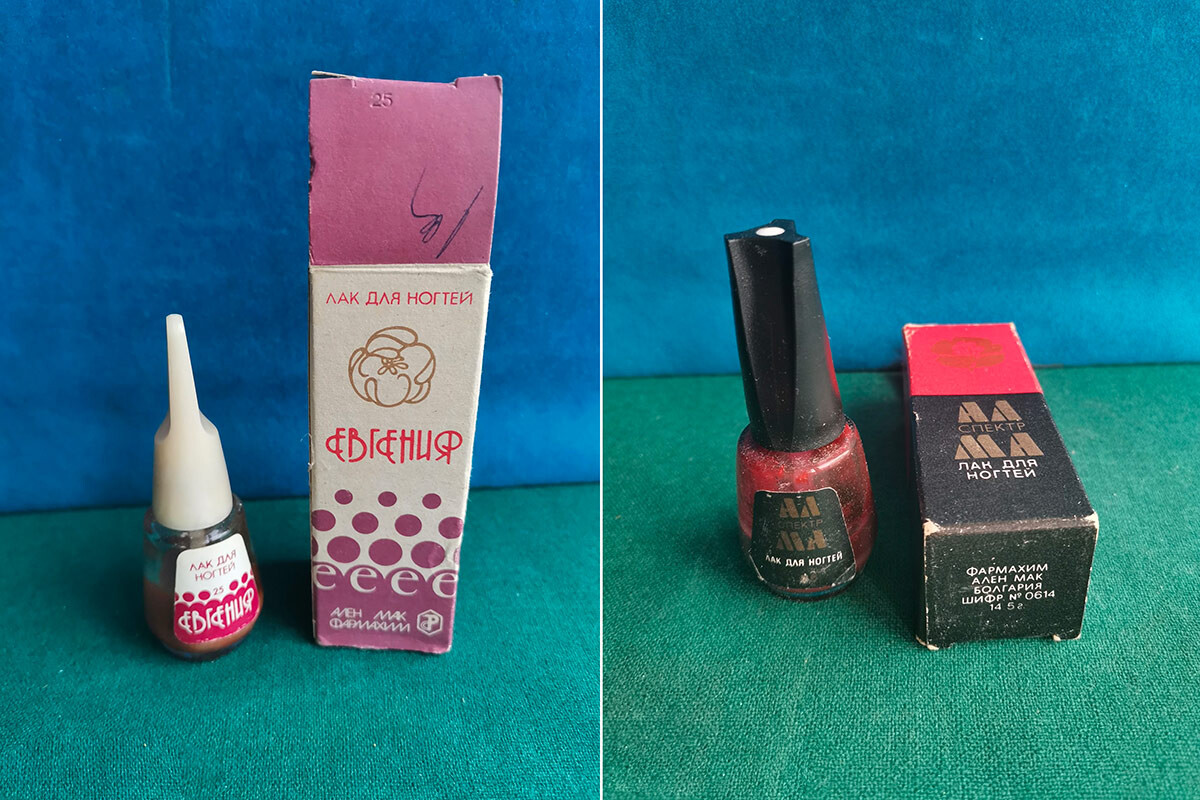 Bulgarian lacquers.
Bulgarian lacquers.
Nail technicians would often mix nail varnishes and add glitter to create unique shades, as there was not always something to their customers’ liking. Also, in the 1970s and 1980s, pearlescent rather than matte colors were the trend.
At the end of the 1970s, imported varnishes were already available in the USSR. The most famous and coveted were French manufacturers Lancôme and Estée Lauder, but also more budget Polish and Hungarian cosmetics were highly appreciated. And while lacquers from socialist countries were widely available on the market, those from Western Europe were quite rare.
How much did it cost?
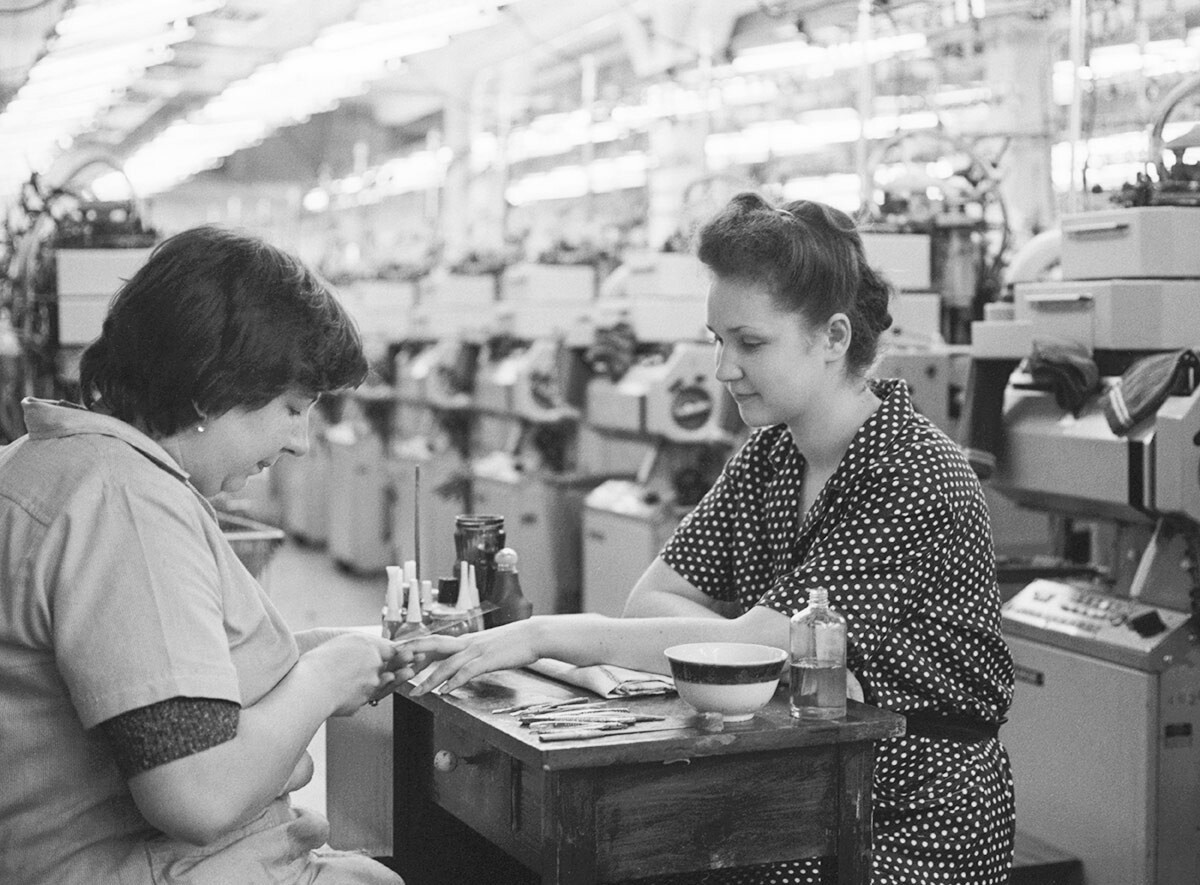 A Chief director of the plant Tamara Ivanyuk manicures the knitter Marina Tyurina. 1987.
A Chief director of the plant Tamara Ivanyuk manicures the knitter Marina Tyurina. 1987.
In Soviet times, the cost of services and goods throughout the country was about the same (except in some rare cases). Moreover, prices were indicated directly on the label tag. For example, in the 1980s, a Soviet nail polish cost approx. 30-80 kopecks (depending on the volume and the manufacturer), which is comparable to the price of a dozen eggs or a couple of loaves of bread. A manicure itself was cheaper, only 20-40 kopecks (with or without coating).
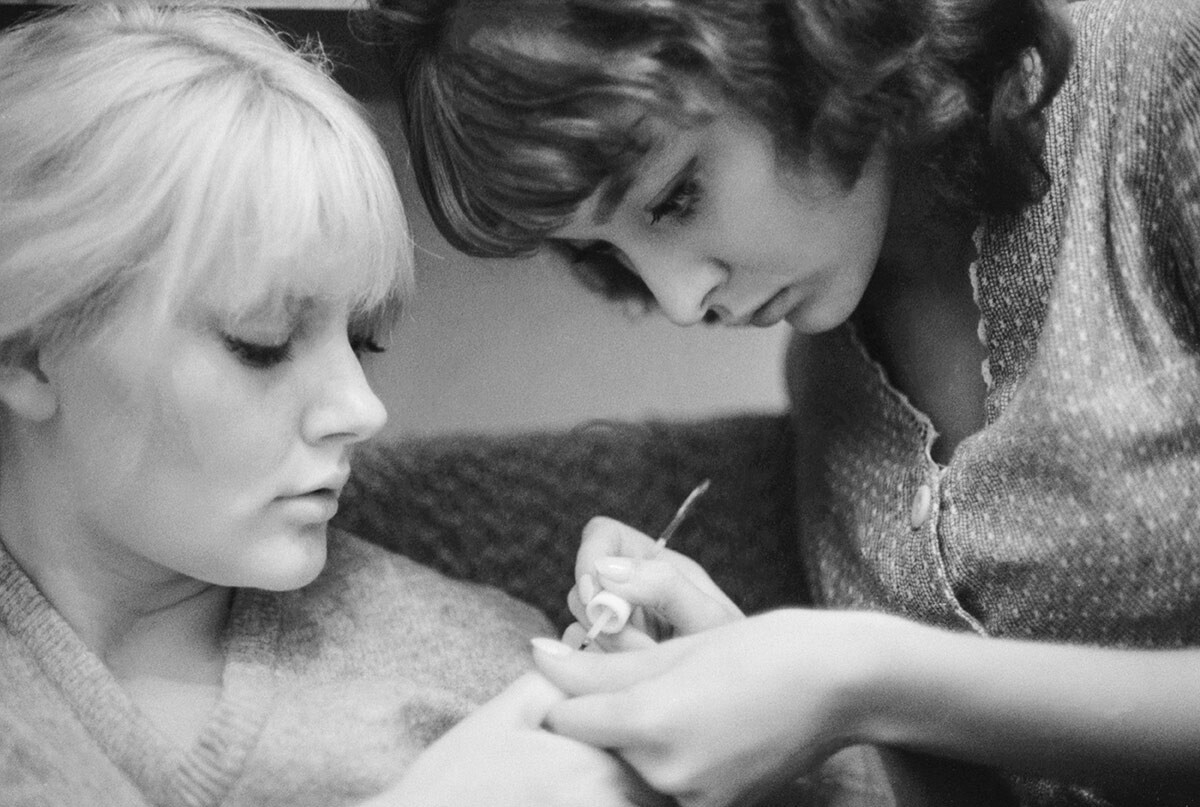 Students of the Shchukin Theatre College of Higher education, sisters Marianna and Anastasiya Vertinsky are making nails, 1964.
Students of the Shchukin Theatre College of Higher education, sisters Marianna and Anastasiya Vertinsky are making nails, 1964.
However, despite the low price of a manicure, it was not done very often, save for some festive occasions. There were usually long waiting lines to nail technicians and not everyone had time to stand in them.
Many women preferred simple home care to that.
Homecare products
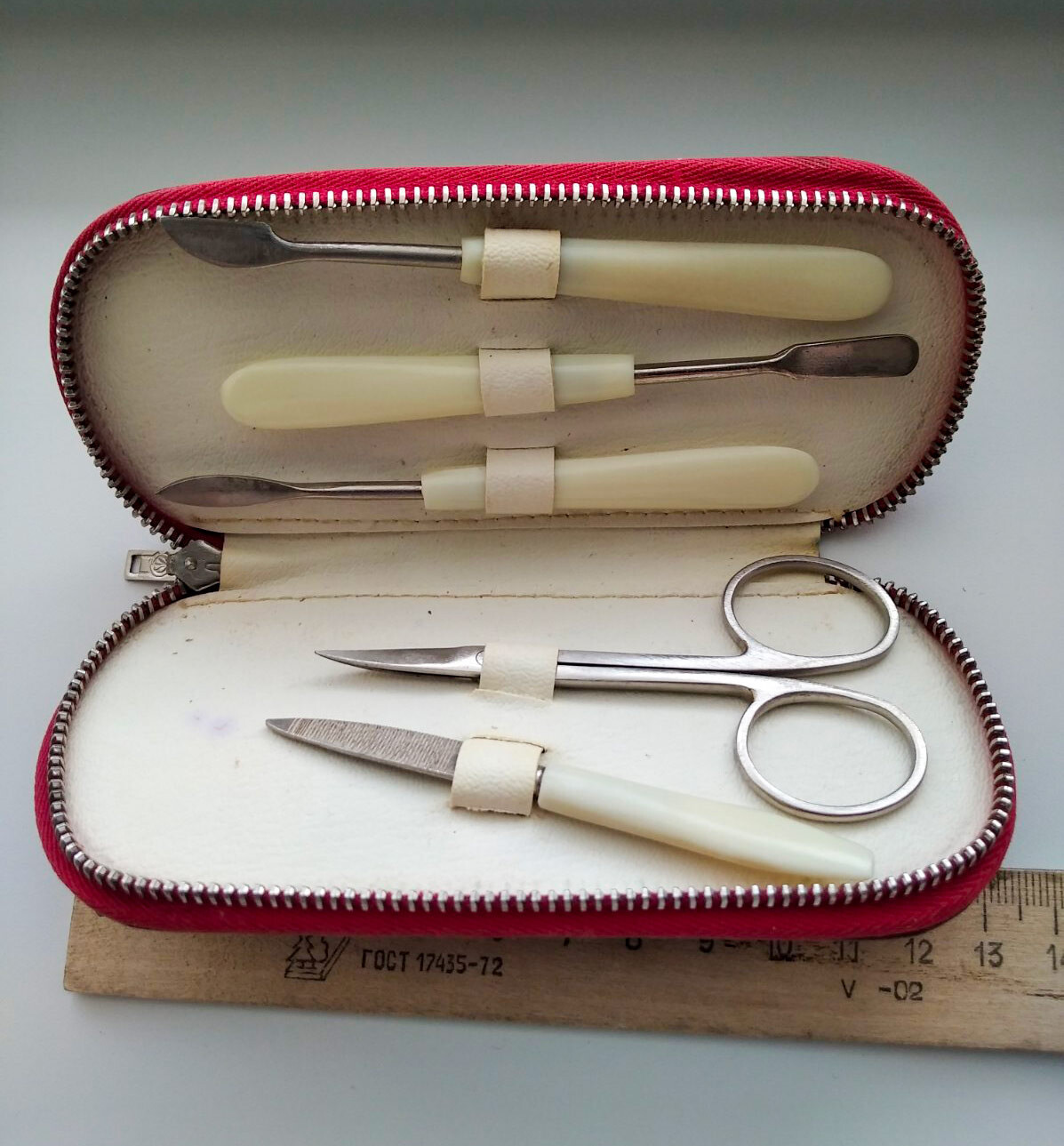 Soviet kit for nails.
Soviet kit for nails.
A good manicure kit at home was something of a must-have in the Soviet times. The major women’s magazine ‘Rabotnitsa’ (as well as books about housekeeping) constantly reminded women of the importance of taking care of their hands. In the first place, the importance of a hygienic manicure (for men, as well) was emphasized. Nails had to be short and clean, without burrs and cuts and to paint them or not was a matter of time and taste.
Kits included the same tools as today, that is, a variety of scissors, tweezers and files to shape the nails and remove the loose cuticles. They would also include eyebrow tweezers or tools for pedicures (which, of course, was also done). All of these were packaged in hard cases and were handy for travel. The cost of a kit was relatively high, about 4-8 rubles, but it was considered a nice gift.













