
Opening Ceremony at the Olympic Stadium. The Russian Olympic Committee (ROC) team with flag bearers fencer Sofya Velikaya and volleyball player Maxim Mikhaylov enter the stadium
Michael Kappeler/dpa/Global Look PressThe world is curious why Team Russia is not performing at the Tokyo 2020 Games. Instead, there is a team called the ‘Russian Olympic Committee’ (ROC). Well, in short, this was done in the aftermath of the doping scandal and a ban of Russian athletes from participating in international competitions under the Russian flag.
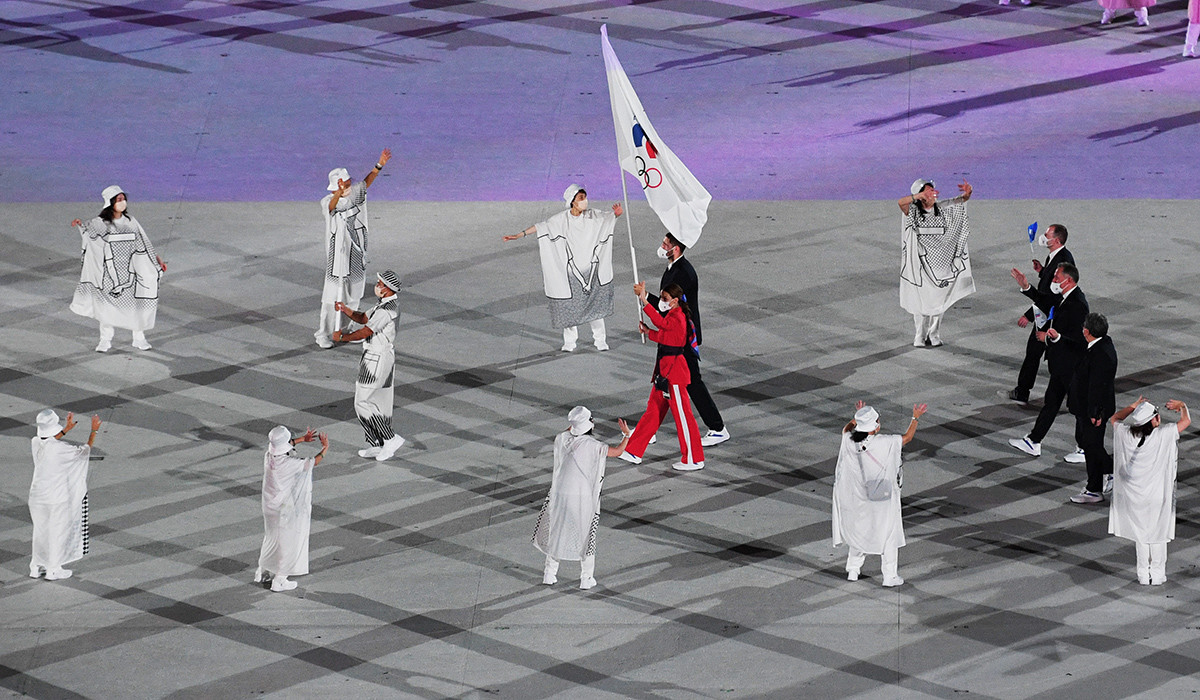

Flag-bearers Sofya Velikaya and Maxim Mikhaylov of the Russian Olympic Committee team lead their country's contingent during the opening ceremony of the Tokyo 2020 Olympic Games
Alexey Filippov/SputnikDespite Team Russia being officially banned, the athletes and the committee found a way for Russian athletes to participate at the Tokyo 2020 Games (which were delayed to July 2021 due to the Covid-19 pandemic). They asked the International Olympic Committee (IOC) to allow them to perform under the name ‘Russian Olympic Committee (ROC), which doesn’t technically have the word ‘Russia’, which is currently banned.
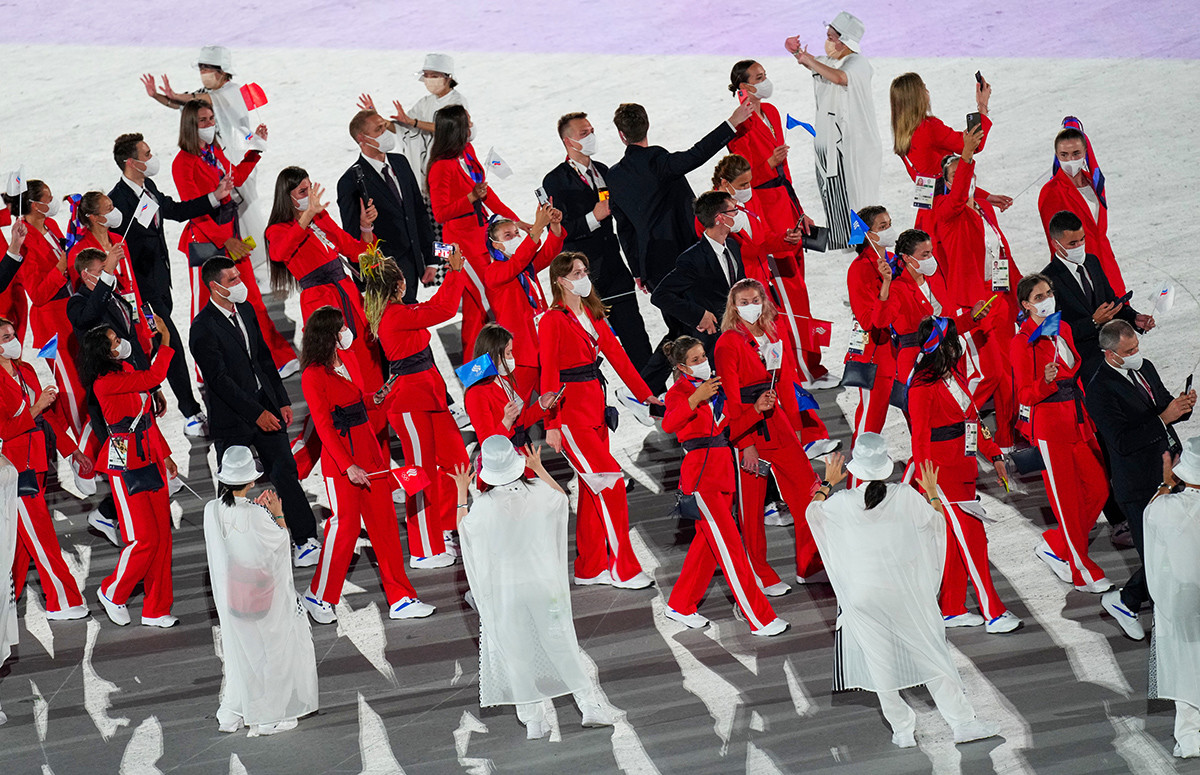

Athletes of the Russian Olympic Committee team march during the opening ceremony of the Tokyo 2020 Olympic Games
Vladimir Astapkovich/SputnikThis way, they also got the chance to use the symbols of the ROC… whose colors refer to the banned Russian national flag. And instead of the national Russian anthem (which was also banned), the IOC permitted a fragment of Pyotr Tchaikovsky's Piano Concerto No. 1 to be played instead.
In fact, the ROC has its own long history… and deserves to act separately. And here’s why.
It was founded in 1911 and celebrated its 100th anniversary in 2011.

The postage stamp marks the anniversary of Russia’s Olympic Committee foundation
GOZNAKAthletes of the Russian Empire didn’t take part in the first three Games of the revived Olympics. Eight Russian athletes participated in the 1908 London Olympics and even won several medals. While, in 1912, the newly founded Russian Olympic Committee sent 178 athletes to the 5th Olympic Games in Stockholm, who participated in all disciplines… but unfortunately did not win any gold medals.
The next Olympic Games after their cancellation during World War I were held in 1920. Russia had already faced the Revolution by that moment, but the International Olympic Committee (IOC) didn’t recognize the new Soviet authorities. So it didn’t send an invitation to the country to take part in the 1920 Games.
While it was already the Soviet Union to boycott the next “capitalist” Games, ignoring the invitations. The Soviet athletes participated in alternative competitions arranged internationally among committees of workers and communists.
The Soviet Union also skipped the first Games after World War II, the 1948 Olympiad in London, as the country had to recover after the war. But the Soviet state was also pushing sports and healthy lifestyles to the masses and had strong athletes, so, soon, the Soviets took a course to integrate in international sports. In 1951, the Soviet Olympic Committee was founded and was at once recognized by the IOC. Soviet athletes performed triumphantly in their first Olympics, the 1952 Games in Helsinki. They won 22 gold medals and managed to score the same amount of points as the United States.
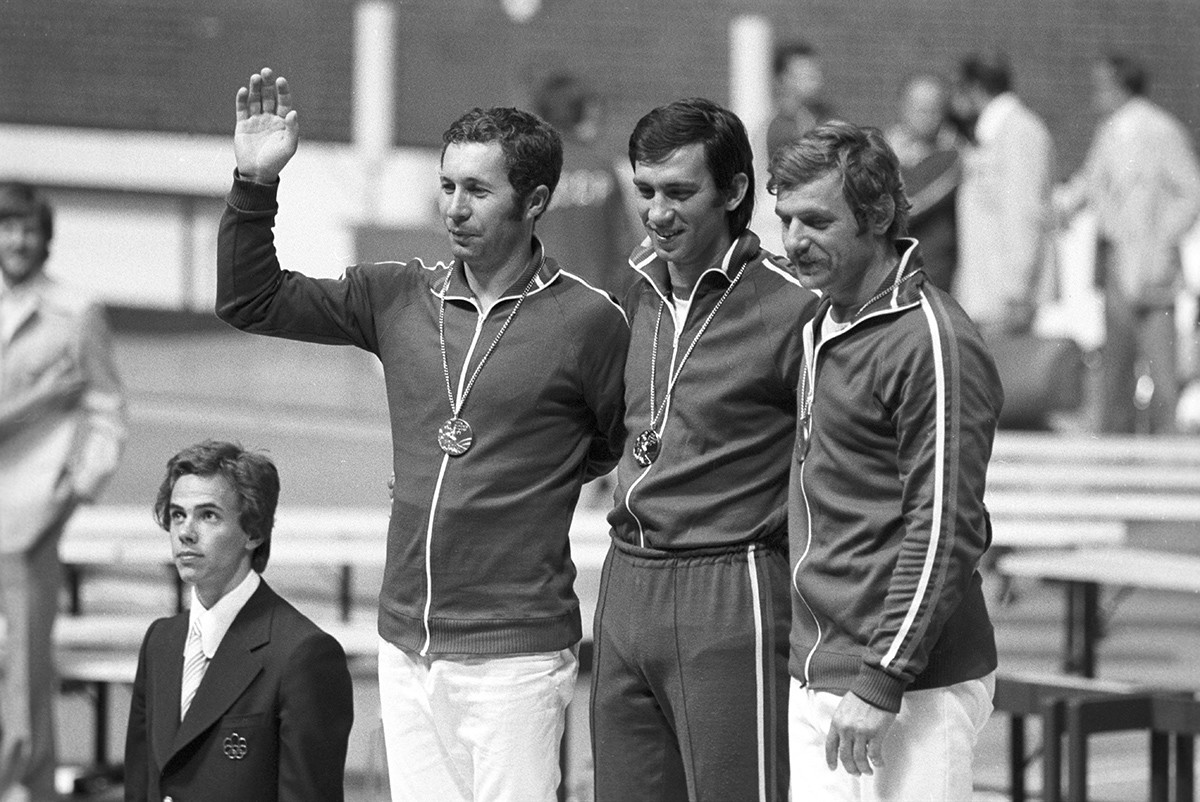

The 1976 Summer Olympic Games in Montreal. Olympic sabre fencing medalists from the Soviet Union, from left: silver medalist Vladimir Nazlimov, gold medalist Viktor Krovopuskov, and bronze medalist Viktor Sidyak.
SputnikIn 1980, the Soviet Union arranged the Summer Olympics in Moscow, which the U.S. boycotted and, in response, the USSR didn’t participate in the next 1984 Games in Los Angeles - it was the only Olympiad the Soviets skipped after the Committee was founded.
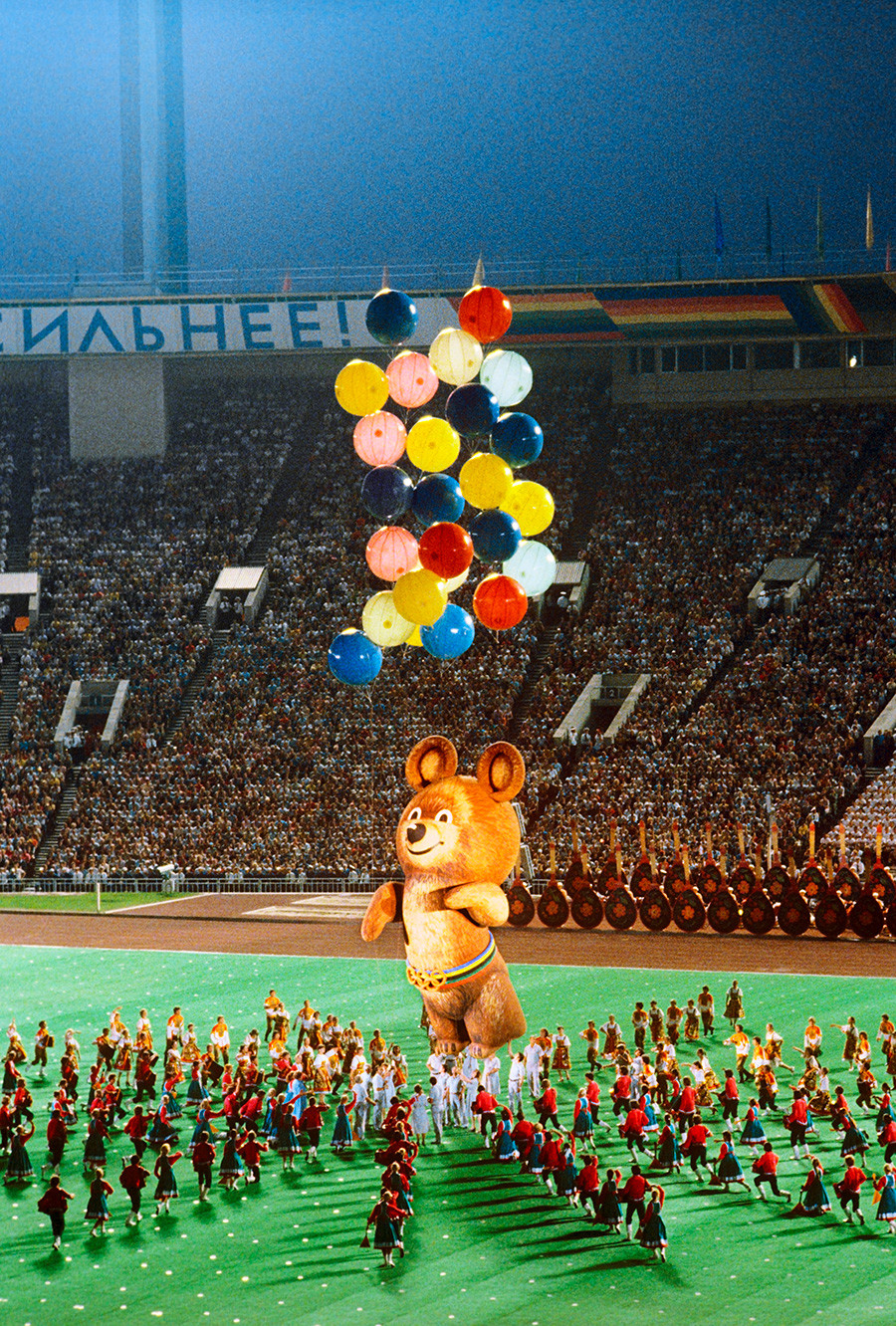
Closing ceremony for 1980 Summer Olympic Games in Moscow. Lenin Central Stadium (Luzhniki).
Sergey Guneev/SputnikIn 1989, even before the Soviet country disappeared, Russia founded its own committee and after the collapse, in 1992, the IOC recognized the Russian Olympic Committee as a successor to the Soviet one.

The emblem of the Russian Olympic Committee
The Russian Olympic CommitteeIn 2014, Russia held its first Olympics in modern history. The preparation for the 2014 Winter Games in Sochi was perceived controversially and international media was very sceptical about it, especially the fact that winter sports would be played in a subtropical city on the seaside. But, despite all that, the Games were a tremendous success.
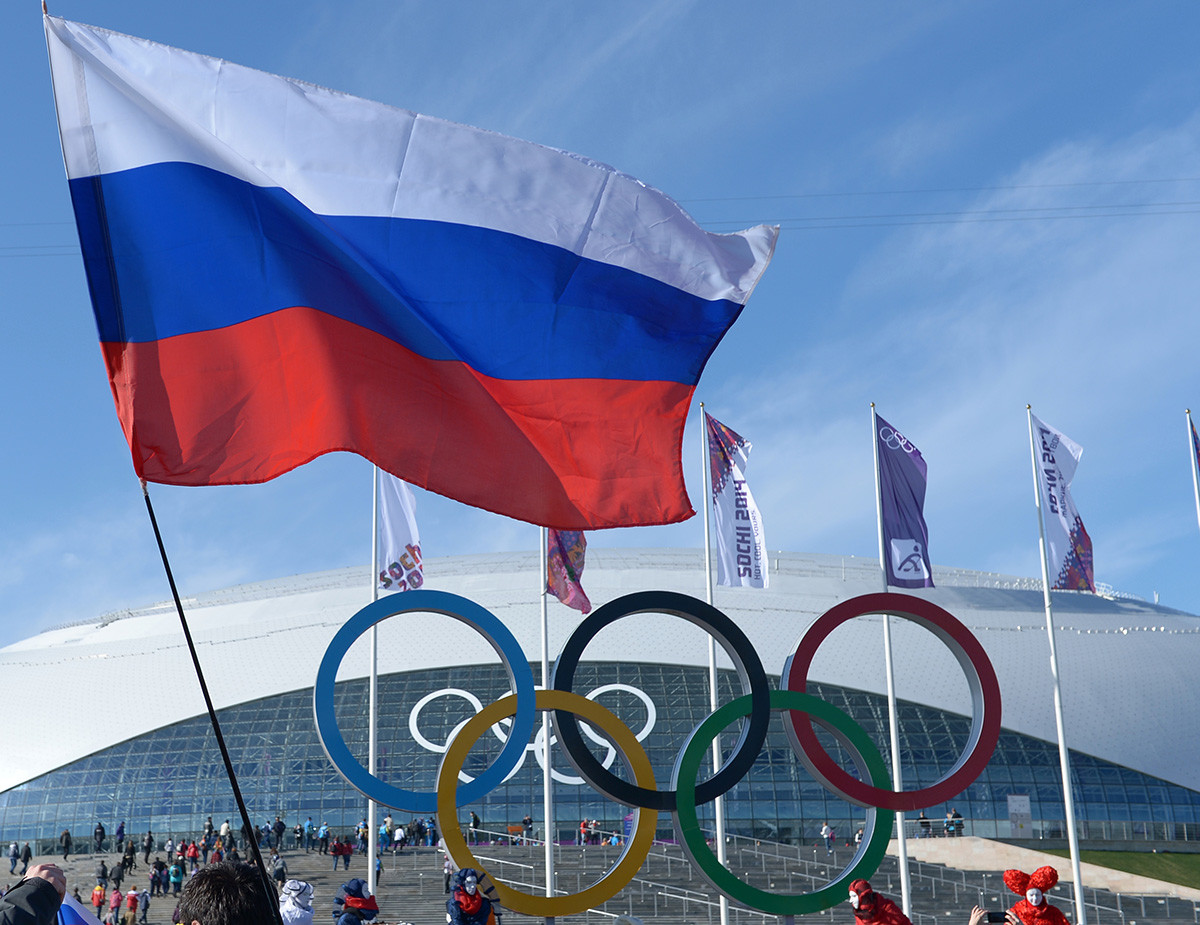

Sport fans with Russian flags in the Olympic Park during the 2014 Sochi Winter Olympics.
Grigoriy Sokolov/SputnikIn 2017, Russia faced a huge doping scandal, suspected of having a state-sponsored doping program and ignoring international Olympic rules. The Russian membership in the IOC was suspended, but restored in 2018, as almost all the athletes had passed the latest drug tests.
In 2019, Russia faced another scandal and the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) sentenced Russia to a four year long ban on participating in any international sports, including the Olympics. Later, in 2020, the Court of Arbitration for Sport allowed Russian athletes to perform in competitions, but on the condition they do not perform under the Russian name, flag, or use the national anthem for the remainder of the ban and perform as “neutral athletes”.
Именно так. «Все повадки гиен пропитаны трусостью: передвигаясь мелкими перебежками, с низко опущенной головой и поджатым хвостом, они приближаются к жертве и нападают исподтишка.»
— Lora (@Lora020563) April 29, 2021
А теперь взгляните на фото! Картина маслом! pic.twitter.com/CpYi0U2rg5
Pictured: A Russian flag hastily removed at checkers championship
So, this is why spectators around the world will watch Russian athletes performing at the Tokyo 2020 Olympics under the mysterious ‘ROC’ title!
If using any of Russia Beyond's content, partly or in full, always provide an active hyperlink to the original material.
Subscribe
to our newsletter!
Get the week's best stories straight to your inbox